This is a library to simulate plate tectonics. It is written in C++ and it has Python bindings (as part of this project), as well as Haskell bindings (hplatec).
Being a library you want probably to use it inside some larger program. From example WorldEngine (a world generator) is based on plate-tectonics.
You can also use the examples to just run the code of this library and generate a few maps. However the examples do not unleash the full power of this library. For running the examples check section Running the examples (C++).
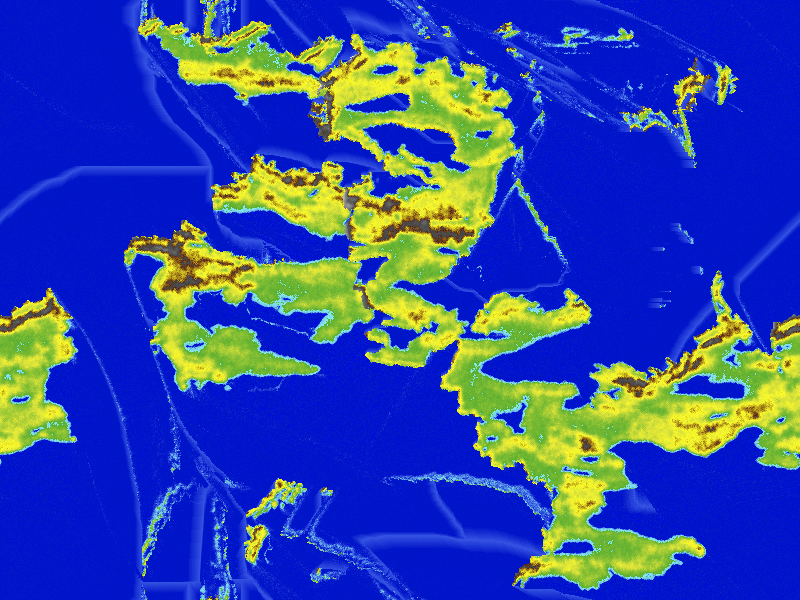
The library offers an API to generate heightmaps and some other data about the world resulting from the simulation. The example permits also to generate maps like this one:
You can see a video of simulation based on an old version of this library: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bi4b45tMEPE#t=0
We use CMake. Install it and then run the folowing commands
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake .. -G "Unix Makefiles"
make
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake ..
make
This should produce a library (libPlateTectonics.a) in the build directory.
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
If you want to build also the examples run:
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake .. -DWITH_EXAMPLES=ON
make
Note: All builds are now done in the build/ directory to keep the source tree clean. The build directory is excluded from version control via .gitignore.
To compile on other platforms please run:
cmake --help
To run also the examples you need to install the library libpng.
From the root directory run:
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake .. -DWITH_EXAMPLES=ON -G "Unix Makefiles"
make
cd examples
./simulationGoogleTest is automatically fetched by CMake using FetchContent, so no manual installation is required.
After building the library with CMake in the build directory:
cd build/test
make
./PlateTectonicsTestsCurrently the test coverage is still poor (but improving!), tests are present only for new code and tiny portion of the old code that were refactored.
Supported versions:
- Python >= 3.9
Install using pip:
pip install PyPlatecThe library is quite simple. platec.create() requires all 10 parameters and supports both positional and keyword arguments:
import platec
# Using positional arguments
p = platec.create(3, 512, 512, 0.65, 60, 0.02, 1000000, 0.33, 2, 10)
while platec.is_finished(p) == 0:
platec.step(p)
hm = platec.get_heightmap(p)
platec.destroy(p)With keyword arguments for clarity:
import platec
# Using keyword arguments (recommended for readability)
p = platec.create(
seed=3,
width=1000,
height=800,
sea_level=0.65,
erosion_period=60,
folding_ratio=0.02,
aggr_overlap_abs=1000000,
aggr_overlap_rel=0.33,
cycle_count=2,
num_plates=10
)
while platec.is_finished(p) == 0:
platec.step(p)
hm = platec.get_heightmap(p)
platec.destroy(p)If you need to build from source instead of using pre-built wheels:
cd pybindings
python setup.py build
python setup.py installFor development:
pip install -e .This project uses C++ linters to maintain code quality. See LINTING.md for details.
Quick start:
# Run all linters
./run_linter.sh
# Run specific linter
./run_linter.sh clang-tidy
./run_linter.sh cppcheck
# Format code
./run_astyle.sh- Improve the quality of the code and add some tests
- Support Google protocol buffer
WorldEngine, a world generator
Widelands, a free, open source real-time strategy game
A fork of platec http://sourceforge.net/projects/platec/ . That project is part of a Bachelor of Engineering thesis in Metropolia University of Applied Sciences, Helsinki, Finland. The thesis is freely downloadable from http://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:amk-201204023993 .
Kudos to the original author: Lauri Viitanen!